Visualization
High quality 2D/3D visualization
Based on industry recognized visualization library VTK (Visual
Tool Kit) and OpenGL, MATFOR graphics library has extended the
limit of data visualization to your astonishing imagination. Complicated
data exhibition like streamline, surface plot, isosurface plot,
vector plot, and slicing plot can be easily created in a few lines
of programming. MATFOR focuses on optimizing the quality of visualization
for plotting any sort of data. Figure 1 illustrates a series of
isosurface plots that are stacked based on meteorological radar
data with multiple altitudes to form a high quality weather map.
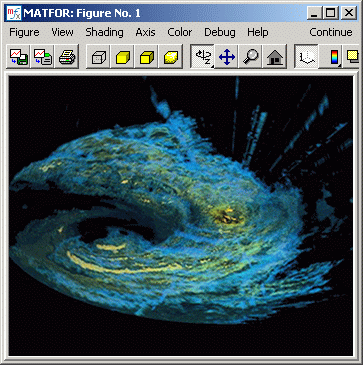
Figure 1: Isosurface Plot
Instant visualization
Unlike other graphics libraries such as OpenGL, MATFOR graphics
library provides a user-friendly and simple environment for implementation.
Without going into the trouble of Windows programming nor being
trapped into low-level graphical routines, computed data is visualized
by simply inserting graphical commands with data of interest as
the input arguments. No previous Windows or graphics initialization
is needed. Time is saved due to the design of automatic initialization
with default environment setting. As a result, you may find your
visualization pops out on the screen instantly. Example 1 illustrates
how the mesh plot procedure is embedded in Fortran programs.
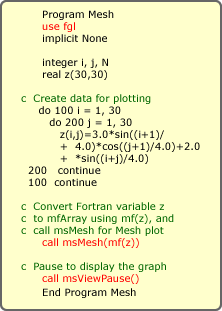
Example 1: Mesh Plot embedded in Fortran program
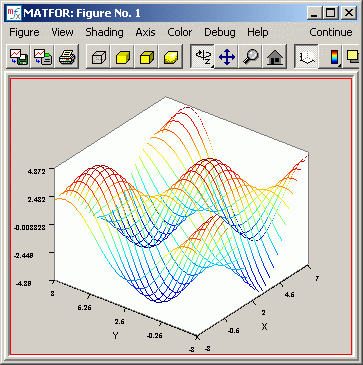
Figure 2: Result of Mesh Plot
Movie-like presentation
Movie-like presentation capability creates a dynamical way of
thinking at your simulation. MATFOR provides recording approach
for the presentation. Pictures displaying on screen can be captured
and saved into a movie file in format like avi (Audio Video Interleave).
Such files can be replayed using media players.
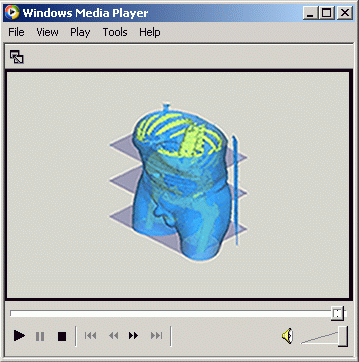
Figure 3: Recorded Animation Playing on Media Player
Speed
Post-processing acceleration
Scientific computing researchers can only debug or do error checking
at the end of each program execution. Chung-Shan Institute of
Science and Technology reveals that when doing CFD (Computational
Fluid Dynamics) researches, 70% of time is spent on post-processing
(e.g. data format conversion, data export, colormap adjustment,
view angle adjustment and visualization debugging), because computed
data can only be visualized for examination after huge quantity
of data is processed. Therefore, real-time program monitoring
mechanism becomes a necessity for scientific computing programmers
as it aids them in reducing the time and effort spent on post-processing.
While the efficiency of MATFOR's graphical procedures is consistently
being optimized, MATFOR focuses on enabling a real-time program
monitoring mechanism for debugging purpose. To achieve this goal,
MATFOR provides Graphics Viewer and Data Viewer that display intermediate
data. During execution, you can 1) see how the algorithm runs
on the Graphics Viewer, 2) pause the algorithm and export intermediate
data to spreadsheet-like Data Viewer for further examination.
"Real-time program monitoring mechanism helps us to save
at least 60% of developing time in each project", says
Dr. Huang of Chung-Shan Institute of Science and Technology.
Simplicity
Single data typing
MATFOR adopts the simple calling concept that is used in Matlab
by introducing state-of-the-art data type called "mfArray". It
is a highly flexible array that does not require explicit data
typing nor dimensioning. Such single data typing brings simplicity
in calling routines, as the one used in Matlab and Visual Basic.
mfArray provides dynamic data typing
and dimensioning in Fortran environment. Most of our procedures
are based on it. mfArray-based procedures can be easily embedded
into your program without any modification to your source code.
It also allows you to use Matlab-like syntax in Fortran environment.
Example 2 shows how mfArray is declared and used.
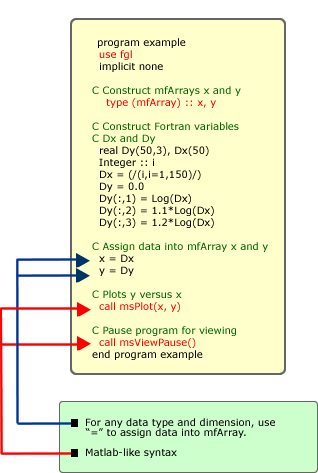
Example 2: Declaration and Usage of mfArray in Fortran
Numerical library
The MATFOR Numerical Library is a collection
of mathematical procedures, ranging from elementary mathematical
procedures such as mfSin, mfCos, and complex arithmetics, to sophisticated
procedures like eigenvalues, lu decomposition, matrix inverse
and conditioning procedures.
Based on Intel?s MKL(math
kernel library), the Numerical Library is promised to deliver
high accuracy and high performance. The Numerical procedures
are organized into several smaller import library sets ?
elfun, fileio, datafun, elmat, and matfun. Most procedures use
mfArray as input and output argument. With the easy-to-use syntax,
MATFOR?s procedures fully take the advantage of vector
language programming so they can be called very intuitively.
The following example shows how MATFOR simplifies the code that
is written originally with traditional Fortran.
The Numerical
procedures adopt the easy-to-call syntax. It allows you to fully
focus on the problem solving without having to worry about the
data structure management and input argument handling. Example
3 shows how Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) procedure is called
in MATFOR and LAPACK.
Example 3: Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)


In addition, MATFOR provides specific numerical procedures that
automatically find the optimal way to solve commonly-used numerical
algorithms, such as solving an inverse matrix. This ensures the
robustness and efficiency of the code.
Example 4: Solving
Ax = b, x = mfLDiv(A, b)
Requirements
MATFOR 3 in Fortran for Windows:
Platform:
Windows 98/NT/2000/Me/XP
Compiler: Compaq Visual Fortran 6.6 above, Intel Fortran
7.0 above,Fortran PowerStation 4.0
MATFOR 3 in Fortran for Linux:
Platform: Linux system with
glibc 2.2.5 or 2.2.93 and the 2.4.X Linux kernel
Compiler: Intel Fortran 7.0 above, PGI Fortran
|